This is an old revision of the document!
SMB Hardening
Technical background to the SMB protocol
Server Message Block is susceptible to NTLM relay attacks if packets are not signed. This man-in-the-middle attack hijacks authentications between clients and servers. Authentication can be used to start a session on the server and steal data. The SMB signing explicitly assigns each initiated session to the client. This means that it is still possible to hijack the authentication, but it is discarded as the session is not signed.
In SMBv1, SMB signing is deactivated by default. This protocol is outdated, error-prone, insecure and should generally be switched off. SMBv2 activates SMB signing as the default value, but only uses it if the server or client require it as a prerequisite. This is usually not the case.
| Server | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Client | Requires | Activated | Deactivated (SMBv1) |
| Required | Signed | Signed | Not supported |
| Enabled | Signed | Signed SMBv1, not signed SMBv2 | not signed |
| Disabled (SMBv1) | not supported | not signed | not signed |
This means that SMB signing must be activated on the server as a prerequisite.
Procedure
Step 1 - Deactivate SMBv1
Clients
Clients can be managed via the login script. The status can be queried via Powershell (admin rights required) as follows:
Get-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName SMB1Protocol
SMBv1 can also be deactivated via Powershell (restart required):
Disable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName SMB1Protocol
Server
The same commands apply to servers. A restart should be scheduled in advance.
Step 2 - Optionally activate SMB signing on the client side
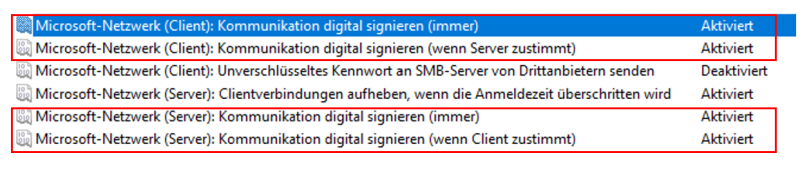
In the next step, SMB signing is optionally activated on the client side. A global group policy can be set for this purpose. The corresponding guidelines can be found here:
Computerkonfiguration ->
Windows-Einstellungen ->
Sicherheitseinstellungen ->
Lokale Richtlinien ->
Sicherheitsoptionen
Alternatively, the settings can also be set in the registry.
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters] "EnableSecuritySignature"=dword:00000001 "RequireSecuritySignature"=dword:00000000
Step 3 - Force SMB signing on the server side
Option 1: via group policy
Computerkonfiguration ->
Windows-Einstellungen ->
Sicherheitseinstellungen ->
Lokale Richtlinien ->
Sicherheitsoptionen
Option 2: via Powershell
Retrieve status
Get-SmbClientConfiguration | select RequireSecuritySignature, EnableSecuritySignature Get-SmbServerConfiguration | select RequireSecuritySignature, EnableSecuritySignature
Enable force
Set-SmbClientConfiguration -EnableSecuritySignature $true Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSecuritySignature $true Set-SmbServerConfiguration -RequireSecuritySignature $true Set-SmbClientConfiguration -RequireSecuritySignature $true
References